Creation year
2022
18 record(s)
Provided by
Type of resources
TETIS Keywords
gcmd Keywords
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Years
Scale
Resolution
Contact for the resource
-
L'atlas cartographique offre un aperçu des données produites et traitées dans le cadre du projet Artisols. Ce dernier, soutenu par la Région Occitanie et le Fonds Européen de Développement Régional (FEDER), s’inscrit dans une démarche d’évaluation et de qualification du processus d’artificialisation des sols en région Occitanie.Neuf grandes thématiques y sont développées : - Les bâtiments résidentiels et d’activité- L’occupation du sol - La densité de bâti par maille de 150 m de côté - L'évolution de la densité de bâti entre 2017 et 2019- Les taches urbaines - La densité de bâti au sein des taches urbaines- Le coefficient de dispersion- L'indice de fragmentation des espaces non artificialisés- L'indice de compacité des taches urbaines
-
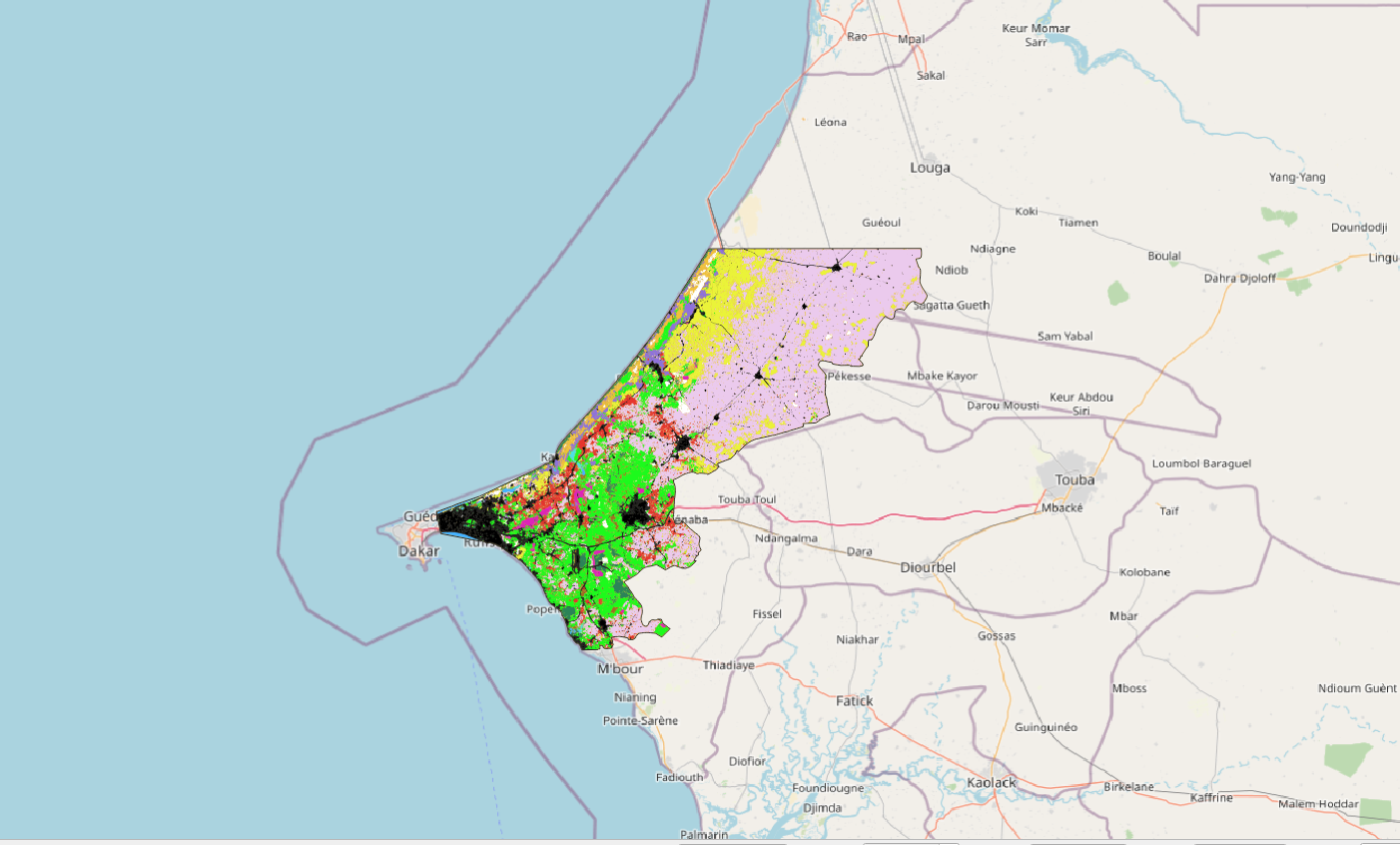
La zone d'étude se situe au nord ouest du Sénégal et s'étale sur 5 100km². Elle inclue la ville de Thiès et une partie de la ville de Dakar, et remonte jusqu'à Kébémer, aux portes du désert de Loumpoul. La carte d'occupation 2018 a été réalisée à partir d'une image à Très Haute Résolution Spatiale (THRS) à 1.5m Spot6 acquise le 15/10/2010 et une série temporelle d'images Sentinel2 (résolution 10m) acquises entre le 01/01/2018 et le 31/12/2018. Le traitement a été réalisé via la chaine de traitement Moringa développée dans l'UMR TETIS. La méthodologie s'appuie sur une Segmentation Orientée Objet de l'image THRS puis d'une classification de chaque polygone (algorithme Random Forest) s'appuyant sur l'image SPOT6, la série temporelle Sentinel2, le SRTM à 30m et de nombreux indices calculés à partir de ces images (NDVI, indices de texture, pente,...). L’algorithme a été entrainé via un jeu de données acquises sur le terrain complété de données obtenues par photo-interprétation. Des corrections manuelles par photo-interprétation ont été réalisées afin d'améliorer le résultat. La précision globale est de 93%. La classification contient 13 classes d'occupation du sol : culture irriguée hors bas-fond, culture irriguée de bas-fond, culture pluviale, plantation, dune sable - arbustes, eau, savane arbustive, savane herbacée, sol nu, sol inondable, sol faiblement végétalisé, végétation naturelle dense et zone urbaine.
-
Les cartographies des espaces bâtis sur la région Occitanie résultent d'une extraction automatique par méthode d'apprentissage profond (deep learning) à partir d'imagerie très haute résolution spatiale (1.5m) SPOT 6/7, pour les années 2015 à 2019. Fichiers fournis sous forme vectorielle. (2021-09-09)
-
Le coefficient de dispersion représente le rapport entre la surface des espaces artificialisés (taches urbaines) morcelés, définis ici pour une emprise inférieure à 3 hectares, et celle des espaces artificialisés denses supérieurs ou égales à 3 hectares.Cet indicateur a été calculé par canton et pour les années 2015 à 2019.
-
La densité de bâti est calculée par maille de 150 mètres de côté et sur la base d'une extraction du bâti à partir d'imagerie très haute résolution spatiale (1.5m) SPOT 6/7, pour les années 2015 à 2019.
-
Les taches urbaines distribuées sont caractérisées par des formes très variées. Ces formes peuvent aller d’un aspect très compacte (proche d’un disque, forme de compacité maximale sur un plan) à celui de formes très digitées ou de filaments, s’approchant de lignes plus ou moins sinueuses. Le suivi de cette dimension de compacité morphologique permet d’estimer si l’artificialisation due aux taches urbaines suit des extensions homogènes ou des extensions hétérogènes. Cet indice est calculé à l'échelle des EPCI d'Occitanie et pour l'année 2019.
-
Le territoire régional est composé de taches urbaines de différentes tailles et formes, distribuées de manière variée. Les espaces urbains sont reliés les uns aux autres par le réseau routier, en particulier le réseau composé des routes primaires et secondaires. Cet espace urbain et routier ainsi composé est fortement artificialisé avec une forte composante d’imperméabilisation qui perdure au fil du temps. La dynamique spatiale et temporelle de cet espace peut être évaluée par les surfaces qui deviennent artificialisées, par la consommation des surfaces interstitielles, généralement agricoles ou naturelles. Ces surfaces à faible imperméabilisation, moins artificialisées, sont ainsi des îlots séparés les uns des autres par la trame urbaine et routière. Ces ilots sont de tailles variées et composent une structure fragmentée.Cet indice prend la forme d'une taille effective de maille, à savoir une grandeur qui exprime « la probabilité que deux points choisis au hasard dans un territoire [...] ne soient pas séparés par des obstacles tels que les voies de communication ou des zones bâties » (J. Jaeger, 2007).
-
Cette donnée raster résulte d'une classification par méthode d'apprentissage profond à partir d'imagerie très haute résolution spatiale (1.5m) SPOT 6/7. Des post-traitements ont été effectués afin de mieux caractériser les classes relatives à l'artificialisation.
-
Les taches artificialisées sont calculées sur la base d'une extraction du bâti à partir d'imagerie très haute résolution spatiale (1.5m) SPOT 6/7, pour les années 2015 à 2019. Deux distances de connexion sont proposées, à 50m et 100m.
-
Les données de nodata par année (entre 2015 et 2019) correspondent aux zones de nuages et de leurs ombres portées sur les images satellites SPOT 6/7 utilisées pour la classification d'occupation du sol, donnée source pour les analyses géographiques qui ont suivi (extraction des espaces bâtis, des taches urbaines, indicateurs spatialisés)
 IDG TETIS
IDG TETIS